SOURCES OF COLLAGEN

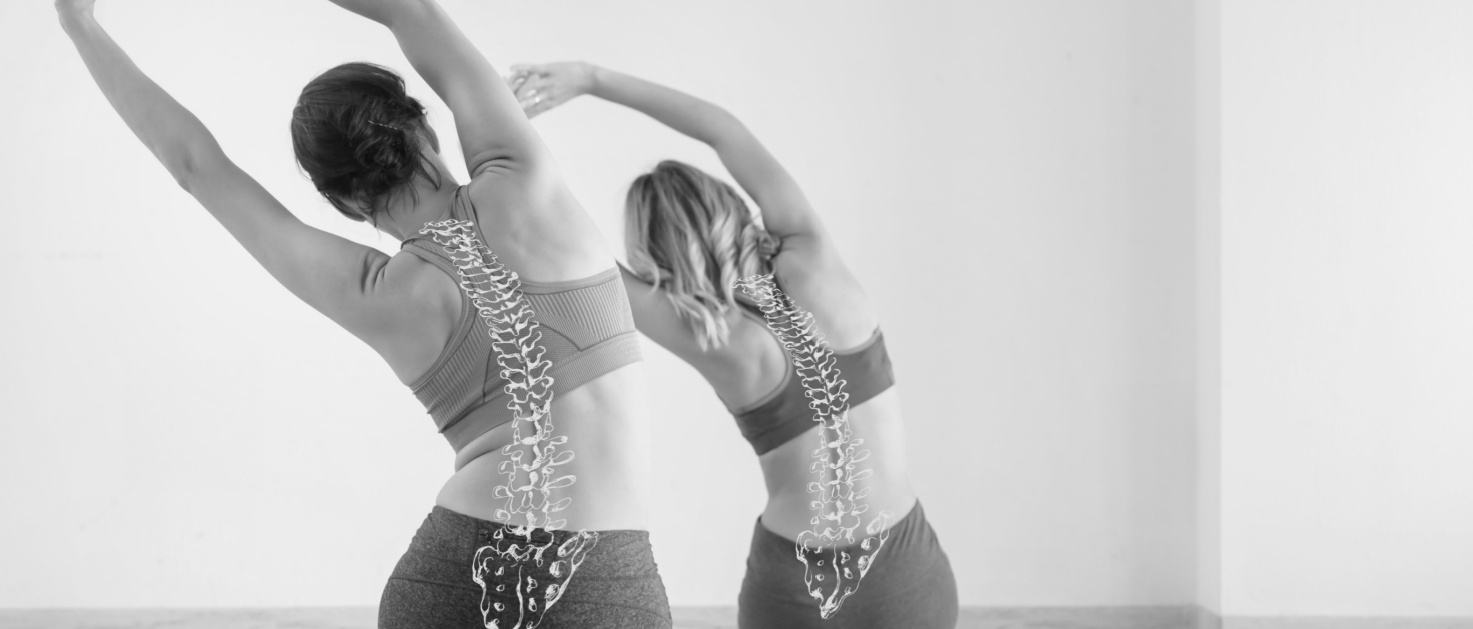
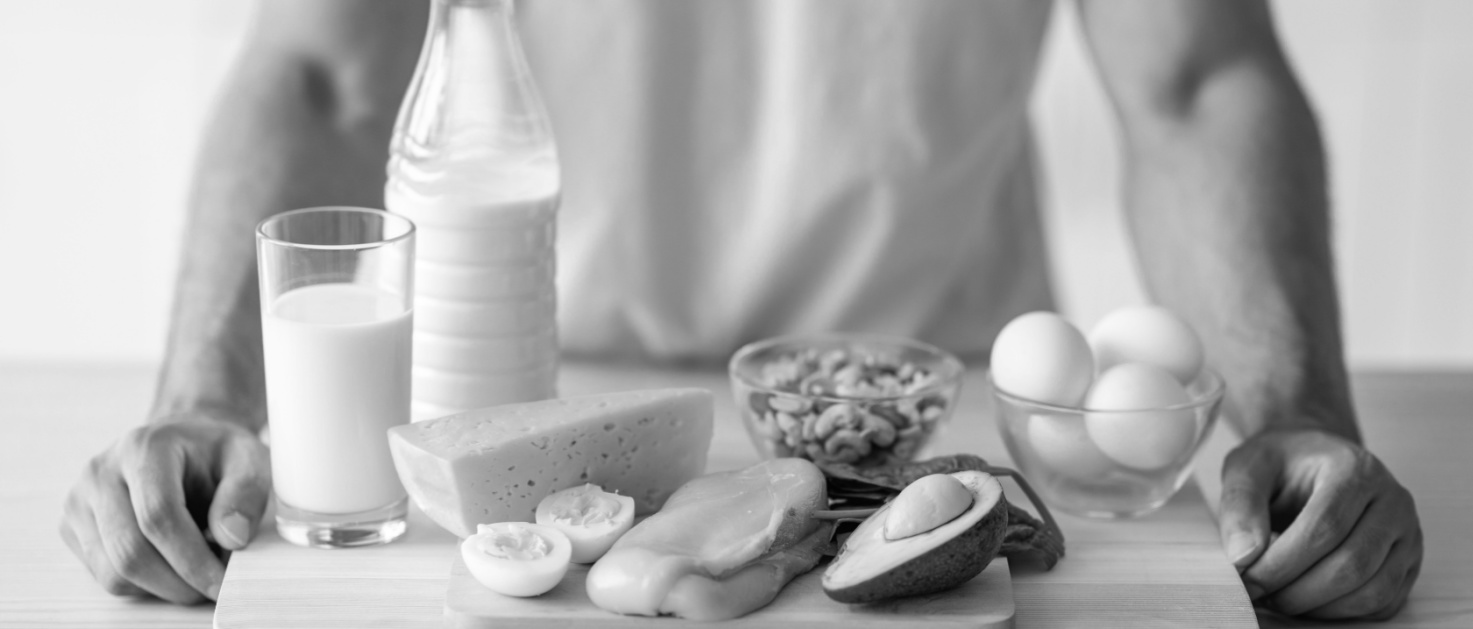
Considering collagen is a natural source of protein found in our bodies, we do not actually need to take supplements. That is, unless we have anti-aging concerns or feel the need to improve joint health or the overall functioning of our bodies. A diet rich in protein derived from poultry, beans, legumes and eggs will ensure that your body’s collagen production isn’t impaired. Bones, skins and ligaments of animals, bone broth, and some seafood like fish skin and jellyfish are high sources of natural collagen however they are not easily consumed. This is where supplements come into the picture. We may choose to take them to improve the health of our skin, joints and hair.
Marine collagen
High in collagen content, marine or fish collagen comes from the skin and scales of fish and is well absorbed by the body, triggering it to boost its collagen synthesis. It is mainly a type I collagen and also has some type II. It works more rapidly than some other sources like bovine collagen. Glycine, the amino acid found in marine collagen improves sleep quality, possibly because it regulates body temperature. Glycine also improves gut health. Marine collagen supports muscle mass and exercise performance as well. It is claimed to be the best option for anti-aging purposes as it helps combat wrinkles, promotes elasticity and increases levels of skin hydration, also strengthening nails and hair.
Bovine collagen
Derived from the bones and hides of cows, bovine collagen is a good source of both type I and type III collagen and is beneficial for joint health. It is recommended along with marine collagen for combatting signs of aging; wrinkles, loss of elasticity and dryness.
Vegetarian / vegan collagen
Although there is no such thing as vegetarian collagen, an alternative “collagen” from non-animal sources is made from genetically modified yeast and bacteria, and notably the bacteria P. pastoris. Human genes are added to the genetic structure of microbes. Once the genes are in place, the yeast and bacteria work toward producing human collagen.
Hydrolyzed collagen
Rather than a source, this is more a process. Collagen used in supplements are usually Hydrolyzed. These are collagen peptides with a shorter chain of amino acids and are primarily composed of type I. Collagen peptides improve skin moisture therefore the rough texture of the skin, softening wrinkles. Hydrolyzed collagen is produced by a process called Hydrolysis where protein is broken into small pieces so that the body can absorb it easily. Collagen peptide powders such as marine and bovine collagen are basically made from “hydrolyzed” collagen which helps with consumption.
Gelatin
Gelatine is widely used in food industries due its features as increasing the thickness, jellification, refining, balancing, foaming, emulsion, stabilization and film-forming. These features are obtained in condition with gelatine’s type, concentration, pH value and working temperature. Gelatine is used mainly in confectionery industries; in the production of jellies, marshmallows and toffees. In addition, it is used as a refining agent in wine and fruit juices, meat and dairy products, and also as a re-inforcing food for sportsmen due to its pure protein content.
GOOD TO KNOW LOST+FOUND
While the loss of collagen in our bodies is inevitable with age, some dietary and lifestyle factors play a significant role in the extent of collagen loss. Smoking, excessive drinking and a diet high in added sugar and processed foods all result in glycation, which means a reduction in collagen turnover. Glycation impedes collagen from interacting with the cells and proteins surrounding it. In order to prevent or minimize this effect, we need to adopt a balanced diet and exercise regularly.
TYPES+USE
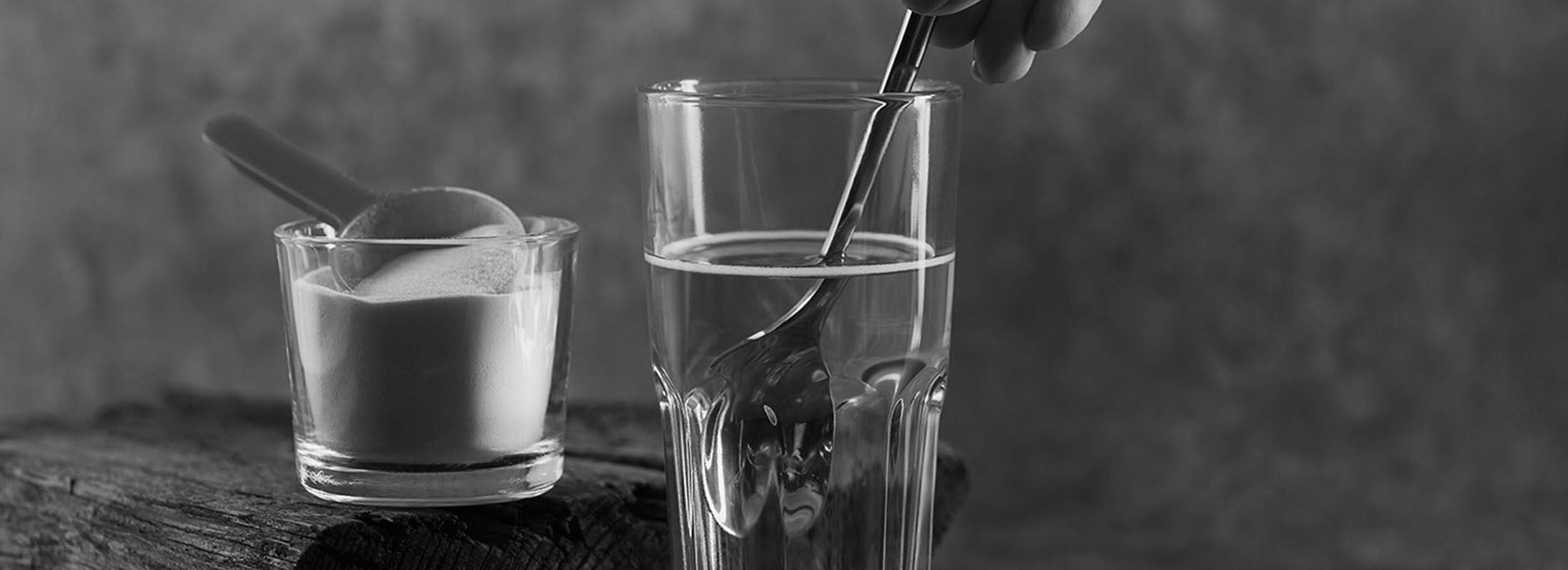
Supplements can be found in liquid, capsule and powder form. Powder collagen can be added to cold and warm beverages like coffee, tea and water. The most popular and perhaps convenient way is to mix them into shakes, matcha tea, oatmeal and yoğurt.
ADD C
Collagen is most efficiently consumed with Vitamin C or hyaluronic acid supplements. Vitamin C deficiency leads to impaired collagen production. Other nutrients that help with collagen synthesis are zinc and copper.
CAUTION
Collagen supplements are normally pretty safe to consume and hardly ever have side effects provided they contain only collagen. Some also contain nutrients like biotin, which might affect the result of certain laboratory health tests. Make sure you read the labels, which is where you will find the suggested dose and be aware of any additional ingredients that may increase health risks.